Introduction
Docker allows your applications to be shipped quickly to any platform running a Docker Engine, and run these applications in an isolated environment called a container.
Docker Engine is a client-server application, which provides three main components:
A
dockerddaemon processREST API which talks to the daemon
Docker CLI
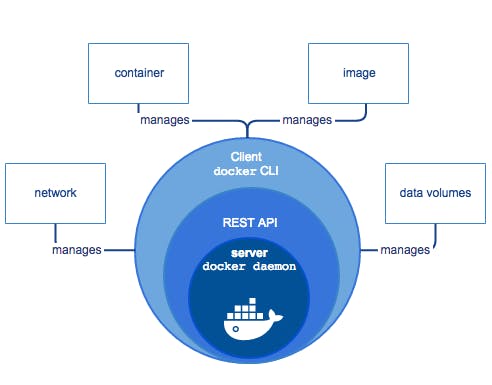
Docker Engine API is a RESTful API, accessible over HTTP, which can be used to develop automation scripts and Docker solutions. Docker Engine API is also available as SDKs for Go and Python programming language.
In this tutorial, you will enable the Docker Engine API and do some Docker operations, like, running a container, listing the logs of the container etc.
Table of Contents
- Pre-Requisites
- Step 1: Enabling the Docker Engine API
- Step 2: Access the Docker Engine API
- Step 3: Running A Container
- Summary
Pre-Requisites
To follow the tutorial, you need to have:
- Docker installed on a Linux system and managed by
systemd
Step 1: Enabling the Docker Engine API
Start by creating a systemd unit file to override the default docker.service unit file.
sudo systemctl edit --full docker.service
Provide dockerd daemon with an additional parameter to expose the API on port 4243
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock -H tcp://0.0.0.0:4243
Reload the systemd daemon to get the new unit file and restart the Docker service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker.service
Step 2: Access the Docker Engine API
Check the version of Docker Engine installed on the system.
curl localhost:4243/v1.41/version
# Output truncated
{
"Platform": {
"Name": "Docker Engine - Community"
},
"Components": [
{
"Name": "Engine",
"Version": "20.10.2",
...
}
Now our Docker Engine API is enabled to listen to HTTP requests. HTTP clients curl or wget can be used to interact with the API.
Step 3: Running A Container
First, pull the alpine image.
curl -X POST "http://localhost:4243/v1.41/images/create?fromImage=alpine:latest"
# Output truncated
{"status":"Pulling from library/alpine","id":"latest"}
...
{"status":"Status: Downloaded newer image for alpine:latest"}
Create the container and grab the container Id. It will be used for the rest of the REST calls.
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"Image": "alpine:latest", "Cmd": ["echo", "hello world"]}' \
-X POST http://localhost:4243/v1.41/containers/create
{"Id":"d4ac7504007","Warnings":[]}
Start the container
curl -X POST http://localhost:4243/v1.41/containers/d4ac7504007/start
See the logs to verify the echo statement printed hello world on the stdout.
curl -o - "http://localhost:4243/v1.41/containers/d4ac7504007/logs?stdout=1"
hello world
Remove the container
curl -X DELETE "http://localhost:4243/v1.41/containers/d4ac7504007"
Summary
Learned how Docker Engine API can be accessed using HTTP clients by providing the additional parameters to the dockerd command in the systemd docker.service unit file. Also created a container which runs the latest alpine image and prints hello world on the standard output.